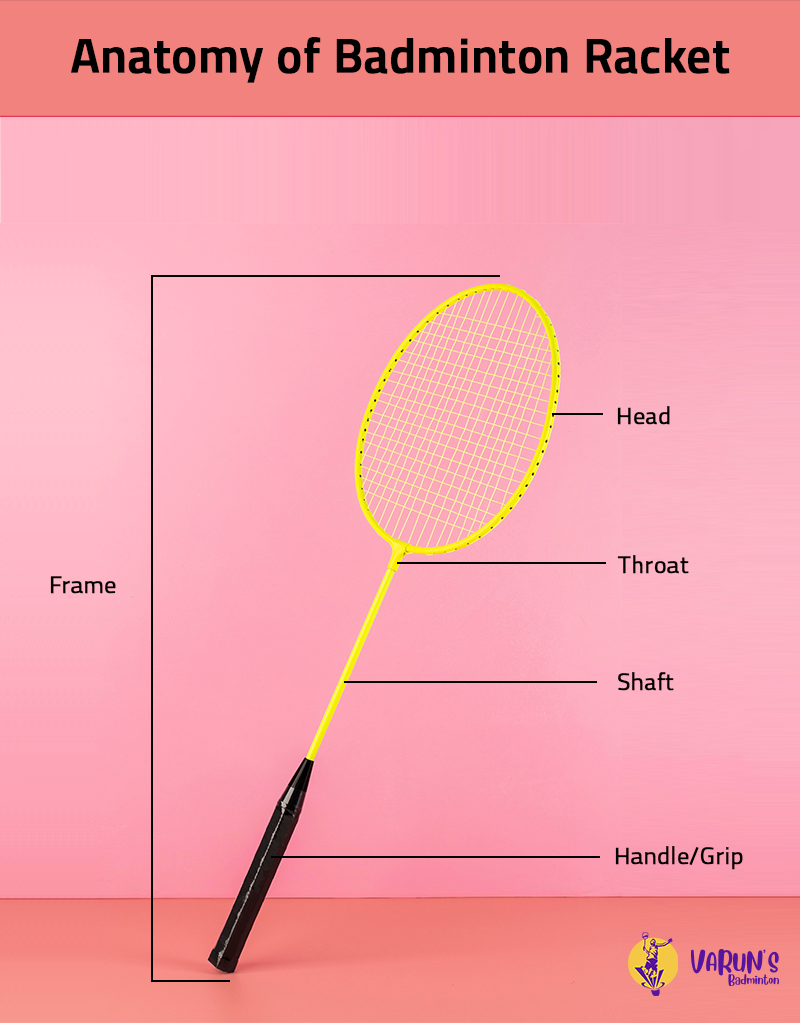
The body of the racket is called the frame. It is a crucial component that influences the overall performance of the racket. Consists of the head, the stringed area, the throat, the shaft and the handle. The frame of the Badminton racket is usually made up of Aluminum or Graphite/Carbon Fiber. Aluminium rackets are generally more affordable. They provide durability and are resistant to scratches and dents and hence more suited for beginners. The Graphite/Carbon rackets are preferred by advanced players. . This offers a better balance between strength and lightness, providing more control and power.
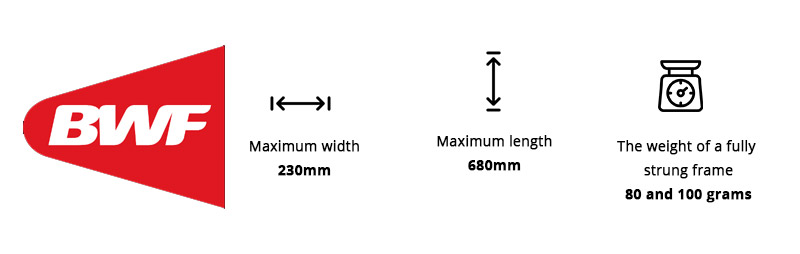
As per the specifications set by the BWF the maximum length of the frame should be 680mm while the width is restricted to 230mm. The weight of the fully strung frame should be within 80 and 100 grams.
The head is the area which bounds the stringed of the badminton racket. Racket heads can have either an oval or an isometric shape. The oval shape of the head have a smaller sweet spot but can provide more control. They are usually preferred by professional players. The isometric head is broader at the top. They have a larger sweet spot offering better performance on off-center hits. This is beneficial for players who are still developing their skills.
The throat connects the head to the shaft of the racket. The throat may be integrated into the head itself or may be a seperate triangular peace at the bottom of the head.
Shaft significantly influences the overall performance and characteristics of the racket. The flexibility of the shaft determines how much it bends during a swing. The shaft can be stiffer or more flexible based on the needs of the player.
Handle also know as the grip is a crucial part of a badminton racket, as it directly connects the player to the racket and influences the overall feel and control during gameplay. The grip come in various sizes ranging from G1 to G5. Players with larger hands may prefer a bigger grip size, while those with smaller hands might opt for a smaller size. The right grip size contributes to better comfort and control. There are two types of grips: The towel grip and synthetic grip. The towel grip are good for absorbing moisture, but may need to be changed frequently; synthetic grips are less absorbent but more durable.
Understanding these components and their interactions is crucial for players to make choices when selecting a badminton racket that suits their playing style and preferences. Players often experiment with different rackets to find the one that optimally complements their skills.

What sets Varun Anand School of International Badminton apart from others is its unwavering commitment to providing a nurturing and motivating environment for its players, fostering their growth, and helping them achieve their full potential in the sport.
S. Varun Anand Head Coach.
RV Sports Academy
2/182A, Norena Gardens, Vadavalli, Tamil Nadu 641041.
+91 98943 18127